Life cycle of thread
Life cycle of thread in java
- Its recommended to learn about life cycle of Thread before you start programming on Thread.
- Threads exists in different type of states.
- Thread having below states.
- New State
- Ready State
- Running State
- Dead State
- Non Runnable States
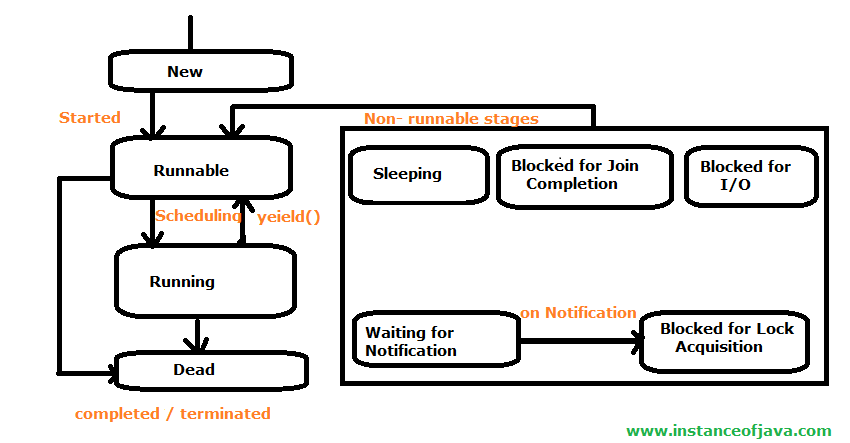
Life cycle of thread in java with diagram
1.New State:
- A thread has been created but not started yet. A thread will be started by calling its start() method.
2.Runnable State:
- This state is also called ready to run stage also called queue. A thread starts in runnable state by calling start() method.
- The Thread scheduler decides which thread runs and how long.
3.Running State:
- If a Thread is executing that means Thread is in Running stage.
4.Dead State:
- Once a Thread reached dead state it can not run again.
5. Non runnable States:
- A Running Thread transit to one of the non runnable states, depending upon the circumstances.
- A Thread remains non runnable until a special transition occurs.
- A Thread does not go directly to the running state from non runnable state.
- But transits first to runnable state.
- Sleeping: The Threas sleeps for specified amount of time.
- Blocked for I/O: The Thread waits for a blocking operation to complete.
- Blocked for join completion: The Thread waits for completion of another Thread.
- Waiting for notification: The Thread waits for notification another Thread.
- Blocked for lock acquisition: The Thread waits to acquire the lock of an object.
- JVM executes the Thread based on their priority and scheduling.
Thread Scheduler:
- Schedulers in JVM implementations usually employ one of these two Strategies.
- Preemptive Scheduling
- Time Sliced or Round robin Scheduling
- Thread schedulers are implementation and platform independent, therefore how thread will scheduled is unpredictable
Thread priority:
- JVM will assign a priority for every Thread created in it.
- 0- will be the minimum priority
- 5- will be the normal priority
- 10- will be the maximum priority
- To hold all these values Thread class has below three corresponding variables
- public static final int MIN_PRIORITY
- public static final int NORM_PRIORITY
- public static final int MAX_PRIORITY
- A thread inherits the priority of its parent Thread. The default priority of the every thread is normal priority 5, because main thread priority is 5.
- We can set the priority of a thread by using setPriority(int priority) method
- public final void setPriority(int priority)
- public void getPriority();
- User defined thread created with default name Thread+<index>, where index is the integer number starts from 0.
- The name of a thread can be change using setName(String name) method.
- Get by using getName() method.
- public final void setName(String name)
- public final String getName().




post a comment