Custom ArrayList in Java
Prerequisite – eks.org or mail your article to contribute@geeksforgeeks.org. See your article appearing on the GeeksforGeek's main page and help other Geeks.
Please write comments if you find anything incorrect, or you want to share more information about
ArrayList in Java
ArrayList in Java (equivalent to vector in C++) having a dynamic size. It can be shrunk or expanded based on size. ArrayList is a part of the collection framework and is present in java.util package.
An ArrayList:
ArrayList <E> list = new ArrayList <> ();
E here represents an object datatype e.g. Integer. The Integer class wraps a value of the primitive type int in an object. An object of type Integer contains a single field whose type is int.
More about Integer Object: here

Custom ArrayList: A custom ArrayList has attributes based on user requirements and can have more than one type of data. This data is provided by a custom inner class that is formed by a combination of various primitive object datatypes.
Consider a case when we have to take input as N number of students and details are:
roll number, name, marks, phone number
A normal method using object ArrayList would be:
// define 4 ArrayLists and save data accordingly in
// each of them.
// roll number arraylist
ArrayList<Integer> roll = new ArrayList<>();
// name arraylist
ArrayList<String> name = new ArrayList<>();
// marks arraylist
ArrayList<Integer> marks = new ArrayList<>();
// phone number arraylist
ArrayList<Long> phone = new ArrayList<>();
// and for n students
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// add all the values to each arraylist
// each arraylist has primitive datatypes
roll.add(rollnum_i);
name.add(name_i);
marks.add(marks_i);
phone.add(phone_i);
}
Now using a custom Arraylist:
The custom ArrayList simply supports multiple data in the way as shown in this image.
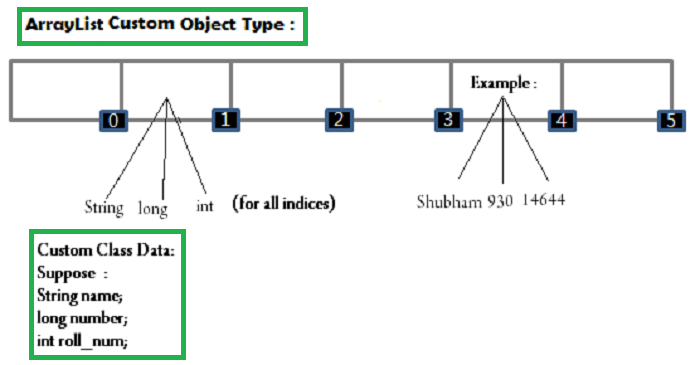
To construct Custom ArrayList
- Build an ArrayList Object and place its type as a Class Data.
- Define a class and put the required entities in the constructor.
- Link those entities to global variables.
- Data received from the ArrayList is of that class type which stores multiple data.
filter_none
edit
play_arrow
brightness_4
|
|
Output:
1 Shubham 100 8762357381 2 Atul 99 8762357382 3 Ayush 93 8762357383 4 Rupesh 94 8762357384
References:
- Oracle documentation
- ArrayLists




post a comment